Parallels nested virtualization has become a pivotal topic in the modern IT landscape, particularly as businesses and developers seek more efficient ways to manage complex computing environments. The concept of running virtual machines within virtual machines is no longer just a theoretical possibility but a practical solution for enhancing productivity, testing environments, and resource management. If you're exploring ways to optimize your virtual infrastructure, understanding parallels nested virtualization is essential.
This article delves deep into the world of Parallels nested virtualization, offering insights into its functionality, benefits, and how it can revolutionize your IT operations. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or a newcomer to the field, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to harness the power of nested virtualization.
By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of Parallels nested virtualization, its applications, and how it can enhance your computing capabilities. Let's dive in and explore this transformative technology.
Read also:Gwenda Swearingen A Comprehensive Look Into Her Life Career And Achievements
Table of Contents
- What is Nested Virtualization?
- Parallels Nested Virtualization
- Benefits of Nested Virtualization
- How Does It Work?
- Use Cases
- Technical Requirements
- Limitations
- Optimizing Performance
- Comparison with Other Tools
- Future Trends
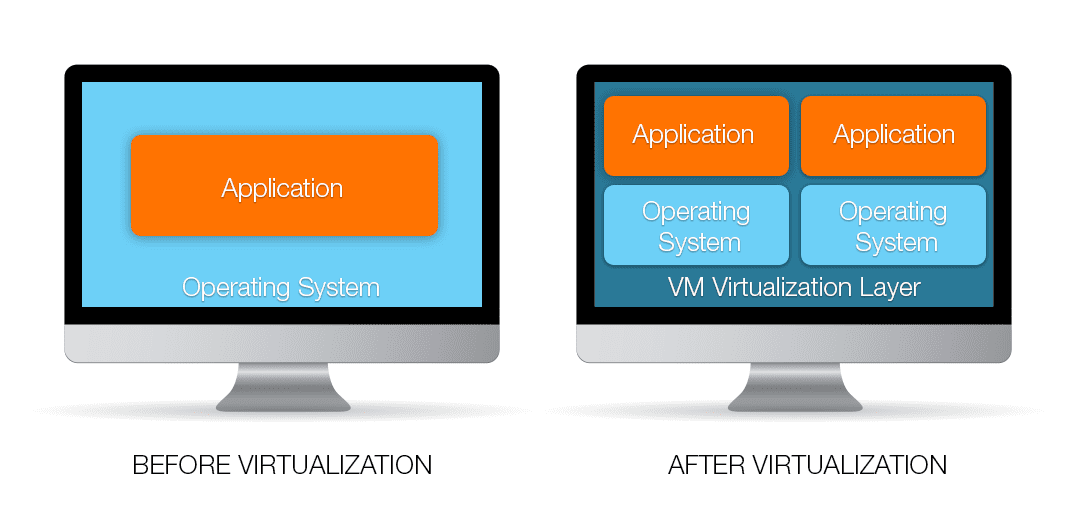
What is Nested Virtualization?
Nested virtualization is a technology that allows virtual machines (VMs) to run within other virtual machines. This concept breaks the traditional boundaries of virtualization, where a hypervisor directly interacts with the physical hardware. Instead, nested virtualization enables a VM to act as a host for additional virtual machines, creating a multi-layered virtual environment.
Key Features of Nested Virtualization
- Layered Architecture: Nested virtualization supports multiple layers of virtualization, allowing complex environments to be created and managed.
- Resource Efficiency: By leveraging the resources of the host VM, nested virtualization optimizes the use of hardware resources.
- Flexibility: It provides flexibility in testing and development, enabling IT professionals to experiment with various configurations without affecting the physical infrastructure.
Nested virtualization is particularly beneficial in scenarios where developers need to test applications in isolated environments or when IT teams need to simulate large-scale deployments for training purposes.
Parallels Nested Virtualization
Parallels offers robust support for nested virtualization, making it an ideal choice for businesses and developers looking to leverage this technology. Parallels Desktop, for example, provides seamless integration with macOS, allowing users to run Windows and Linux virtual machines on their Macs. With nested virtualization, Parallels takes this capability a step further by enabling the creation of virtual environments within these VMs.
Advantages of Using Parallels for Nested Virtualization
- Compatibility: Parallels supports a wide range of operating systems, ensuring that nested virtualization can be implemented across different platforms.
- Performance: Parallels optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that nested VMs perform efficiently without significant overhead.
- Ease of Use: The user-friendly interface of Parallels simplifies the setup and management of nested virtualization environments.
According to a report by Gartner, nested virtualization is becoming increasingly popular due to its ability to enhance productivity and streamline IT operations. Parallels is at the forefront of this trend, providing cutting-edge solutions for modern computing needs.
Benefits of Nested Virtualization
The adoption of nested virtualization brings numerous advantages to organizations and individuals alike. Below are some of the key benefits:
1. Enhanced Testing and Development
Nested virtualization allows developers to create isolated environments for testing applications. This ensures that any changes or updates do not affect the production environment, reducing the risk of downtime and errors.
Read also:Billie Eilish Nude A Comprehensive Look At Misinformation Privacy And Media Sensationalism
2. Cost Efficiency
By maximizing the use of existing hardware resources, nested virtualization helps organizations reduce costs associated with purchasing and maintaining additional physical infrastructure.
3. Scalability
With nested virtualization, businesses can easily scale their operations by adding more virtual machines as needed. This flexibility is crucial for accommodating growth and adapting to changing demands.
How Does It Work?
The mechanics of nested virtualization involve the interaction between the hypervisor and the virtual machines. In a typical setup, the host hypervisor manages the physical resources, while the guest VM acts as a secondary hypervisor, hosting additional virtual machines.
Key Components
- Hypervisor: The software layer responsible for managing virtual machines and allocating resources.
- Virtual Machines: The simulated environments that run on top of the hypervisor, capable of hosting operating systems and applications.
- Resource Allocation: The process of distributing CPU, memory, and storage resources among the virtual machines.
Understanding these components is essential for effectively implementing and managing nested virtualization environments.
Use Cases
Nested virtualization finds applications in various fields, including:
1. Software Development
Developers use nested virtualization to test applications in different operating systems and configurations, ensuring compatibility and performance.
2. IT Training
IT professionals leverage nested virtualization to create realistic training environments, enabling learners to practice complex tasks without impacting real systems.
3. Cloud Computing
In cloud environments, nested virtualization allows service providers to offer more flexible and scalable solutions to their customers.
Technical Requirements
Implementing nested virtualization requires specific hardware and software configurations. Below are some of the key requirements:
1. Hardware Support
Modern processors with virtualization extensions, such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V, are essential for supporting nested virtualization. Additionally, sufficient memory and storage are necessary to accommodate the virtual machines.
2. Software Compatibility
Ensure that your hypervisor and operating systems support nested virtualization. Parallels Desktop, for instance, provides robust support for this feature on macOS.
Limitations
While nested virtualization offers numerous advantages, it also has certain limitations:
1. Performance Overhead
Running multiple layers of virtualization can introduce performance overhead, potentially impacting the speed and efficiency of the virtual machines.
2. Complexity
Managing nested virtualization environments can be complex, requiring advanced knowledge and skills to ensure optimal performance and stability.
Optimizing Performance
To get the most out of nested virtualization, consider the following tips:
1. Allocate Resources Wisely
Ensure that each virtual machine receives adequate resources, balancing the needs of the host and guest VMs.
2. Use Efficient Hypervisors
Select hypervisors that are optimized for nested virtualization, such as Parallels Desktop, to minimize performance overhead.
3. Monitor and Adjust
Regularly monitor the performance of your virtual environments and make adjustments as needed to maintain optimal operation.
Comparison with Other Tools
When evaluating nested virtualization solutions, it's important to compare Parallels with other tools in the market. Below is a brief comparison:
Parallels vs. VMware
- Parallels: Offers seamless integration with macOS, making it ideal for Mac users.
- VMware: Provides robust enterprise-level features, suitable for large-scale deployments.
Parallels vs. Hyper-V
- Parallels: User-friendly interface and strong support for nested virtualization.
- Hyper-V: Built into Windows, offering native support for virtualization on Windows platforms.
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and the platforms you are working with.
Future Trends
The future of nested virtualization looks promising, with advancements in technology driving further innovation. Some emerging trends include:
1. Improved Performance
As hardware and software continue to evolve, we can expect nested virtualization to become even more efficient, reducing performance overhead and enhancing user experience.
2. Enhanced Security
Security measures for nested virtualization environments will likely become more sophisticated, protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of virtual machines.
3. Increased Adoption
With its growing popularity, nested virtualization is expected to be adopted by more organizations, driving the development of new tools and solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Parallels nested virtualization offers a powerful solution for optimizing IT operations and enhancing productivity. By enabling the creation of multi-layered virtual environments, it provides flexibility, cost efficiency, and scalability. However, it's important to consider the technical requirements and limitations when implementing this technology.
We encourage you to explore the capabilities of Parallels nested virtualization and see how it can benefit your organization. Don't forget to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. For more insights and updates, explore our other articles on virtualization and IT solutions.